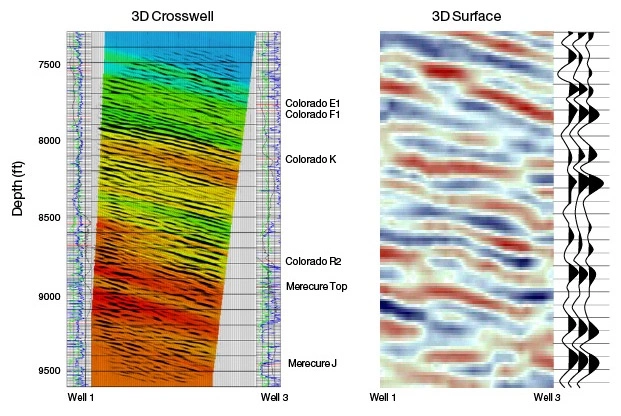
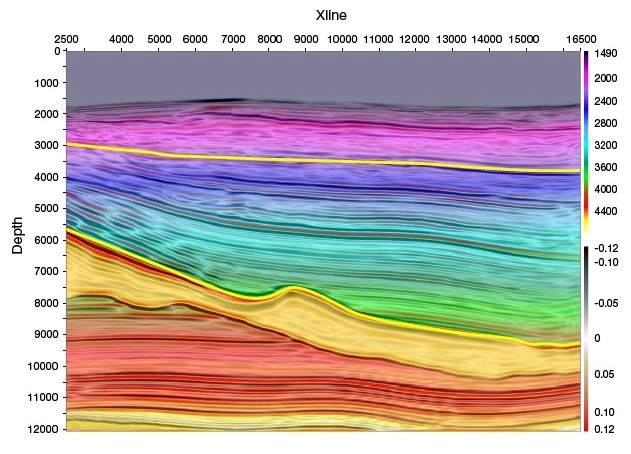
After the core arrives at the laboratory, a detailed core description can be made in optimal working conditions. The description includes: The reservoir rock type ...
Read More »Masonry Layout
Fluid Saturation Determination
The pore spaces in rocks which form oil and gas reservoirs are always completely saturated with fluids. There are never any void spaces within the pores ...
Read More »Permeability Measurement
Learning Objectives After completing this topic “Permeability Measurement“, you will be able to: Discuss the …
Read More »Porosity Measurement | What is porosity and how is it measured?
Porosity is the volumetric void space within rocks, being that space not occupied by solid rock material. Porosity is thus a measure of a reservoir's storage ....
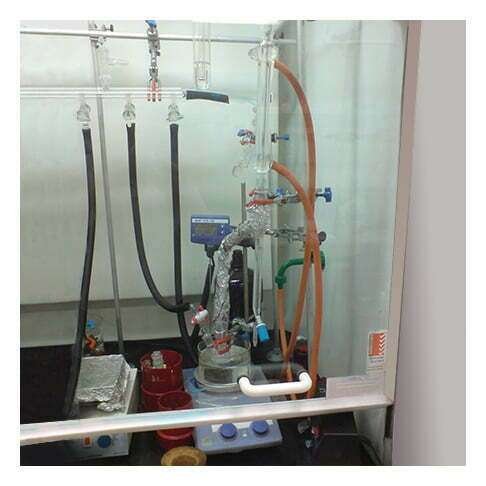
Read More »Core Sample Preparation
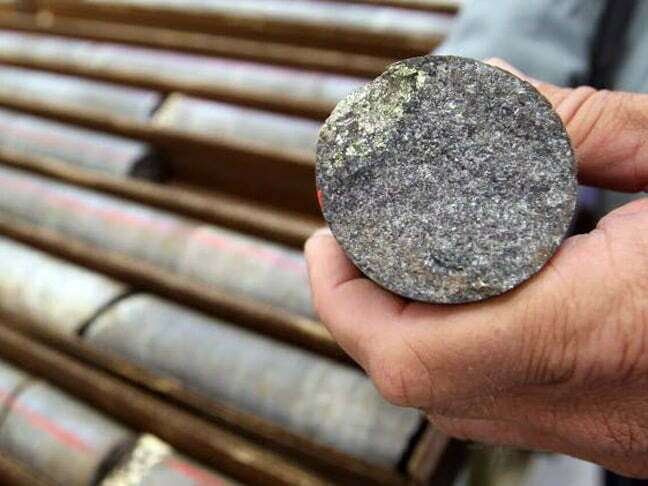
The analysis of rock cores (Figure 1) plays a major role in helping geoscientists and reservoir engineers to determine a reservoir’s hydrocarbon storage capacity and ...
Read More »Introduction to Core Analysis
Cores are direct samples from the reservoir rocks that can be tested, analyzed, and viewed by the researcher. A core analysis project starts from the coring plan ...
Read More »Interpretation with Seismic Attributes
Learning Objectives After completing this topic “Interpretation with Seismic Attributes”, you will be able to: …
Read More »Seismic Interpretation Methods
Learning Objectives After completing this topic ” Seismic Interpretation Methods “, you will be able …
Read More »Seismic Stratigraphy
Learning Objectives After completing this topic “Seismic Stratigraphy“, you will be able to: Determine what …
Read More »Structural Interpretation
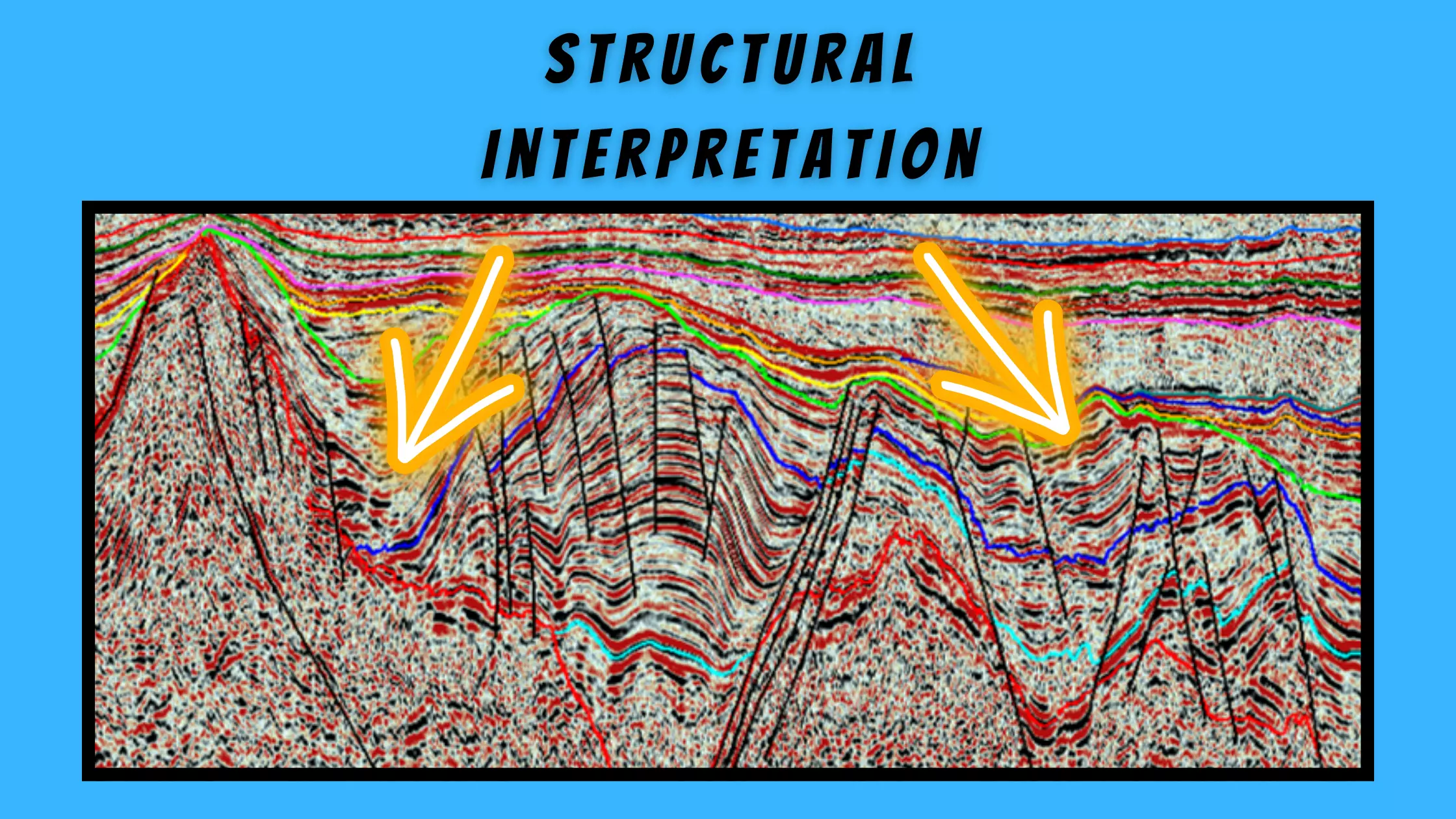
The initial goal of seismic structural interpretation is to determine the location of favorable traps for hydrocarbon accumulations. The first step is to determine ...
Read More » Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.