Handling Unexpected Changes in Geology
Many geologists with ample experience in drilling horizontal wells will say that they thought they knew a prospect very well -until their horizontal well was drilled (Figure 1: Refining the reservoir concept through horizontal drilling).

(In some cases, it might be claimed that LWD actually stands for Learning While Drilling.) Before the advent of horizontal drilling, a well was drilled to predefined target points (obtained mainly from geological/geophysical interpretation) in the reservoir. The geologist only had to solve a one-dimensional problem, and had only one opportunity to be wrong. Either the top of the prospective reservoir would be where it was predicted or it would not. The prospect was then completed or plugged, and the geoscientist went on to the next project.
Now, with horizontal wells, the geoscientists must consider their problem in at least two dimensions, and often in three. This means that they have the opportunity to be wrong several times a day, for weeks on end.
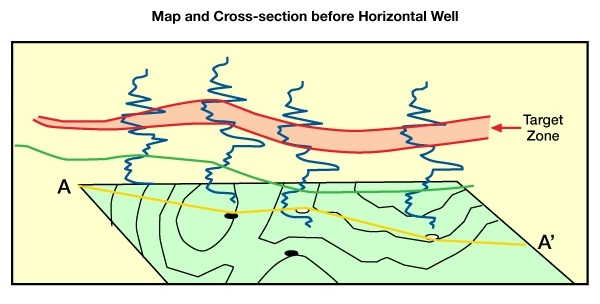
Figure 2 shows an example of a cross-section drawn on a prospect map, with correlation curves from four wells projected above the section.
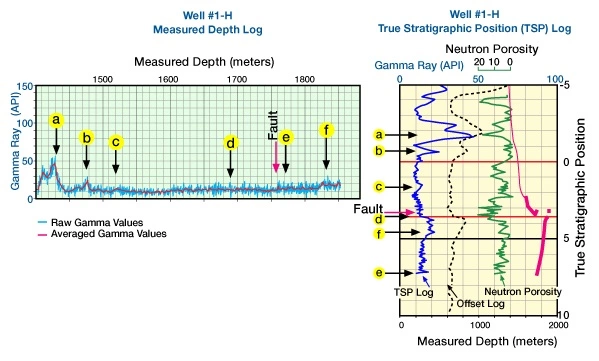
An LWD log was generated while drilling a horizontal well on this prospect. The log revealed an unanticipated fault (Figure 3).
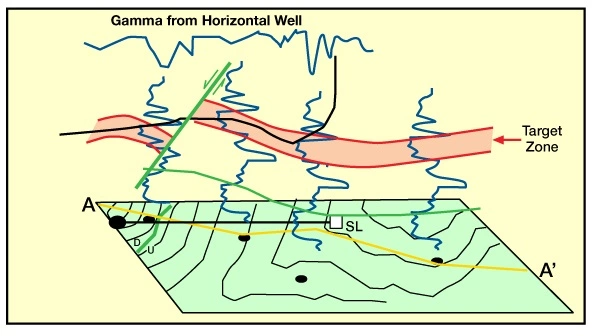
As a consequence, the overall prospect interpretation had to be re-drawn (Figure 4).
The lesson to be learned is that pre-drill planning should be prepared with enough flexibility to accommodate unforeseen changes in geology. Contingency plans should be in place to provide the best outcomes.
Recommended for You
Drilling Measurements and Logging Tools in Geosteering
Assessment
Which of the following is not among the purposes of optimum wellbore planning?
A .Create a plan that is perfect and will not need any adjustment during the drilling of the well. Correct
B .Make certain that all stratigraphic objectives will be met as the horizontal wellbore is drilled.
C .Ensure that all personnel are available that will make the horizontal well a success.
D .Ensure that the correct evaluation tools are on bottom that will provide all of the data needed to evaluate stratigraphic goals.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



