Learning Objectives
After completing this topic “Plug Cementing”, you will be able to:
- Define plug cementing and associated terms.
- Summarize the reasons for setting plug cementing (Cement plugs).
- Describe the types of plug cementing (Cement plugs) and the context within which they are used.
- List the major considerations involved in designing a cement plug job.
- Describe methods for evaluating the success or failure of a cement plug job.
- Perform simple volume/displacement calculations, in particular using balanced plug method.
- List circumstances under which a cement plug can fail.
What is a Plug Cementing?
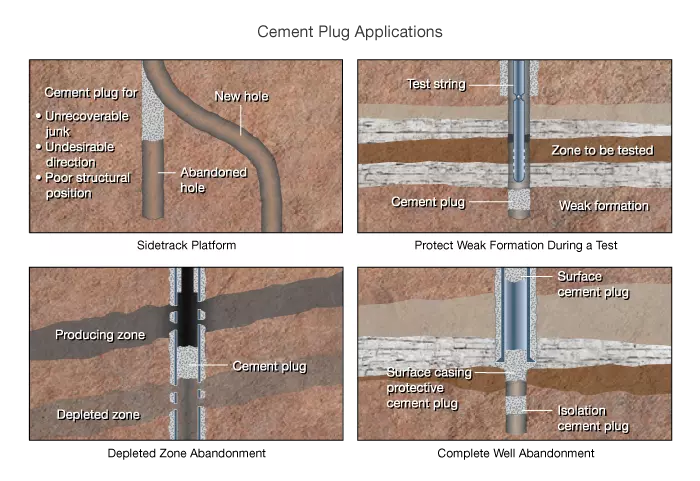
Plug cementing is the placement of cement within a wellbore or casing to prevent flow. There are several common reasons for setting a cement plug in a well (Figure 1):
- Complete well suspension or abandonment
- Depleted zone abandonment
- Sealing off lower intervals in a well so that the well can be sidetracked or recompleted in a shallower zone
- Protecting weak formations from high pressure operations that may take place in shallower intervals
Cement plugs can also be used during drilling operations. For example, in cases of lost circulation during drilling, a cement plug can be spotted to seal off the loss zone. In rare situations cement may be used as a means of well control during the drilling process if the well is at a point where there is no difference between pore pressure and fracture pressure.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



