Clay Classifications
Clay can be classified by examining the following three characteristics:
- Mineralogy
- Grain size
- Origin
Clay Classification According to Mineralogy
Common clay minerals can be classified into broad types, each having a similar base structure while exhibiting a wide range of compositions. On a molecular level, these minerals are arranged into sheets of alumina-octahedron and silica-tetrahedron lattices (Figure 1). The four major types of clay minerals that are commonly found within the pore system of sandstones are smectite (montmorillonite), illite, kaolinite and chlorite. Figure 2 shows microscopic photos of the four types. The most important aspect of these minerals with regard to petrophysical interpretation, is their ability to hold adsorbed water on their grain surfaces, which complicates the determination of the fluid saturation.
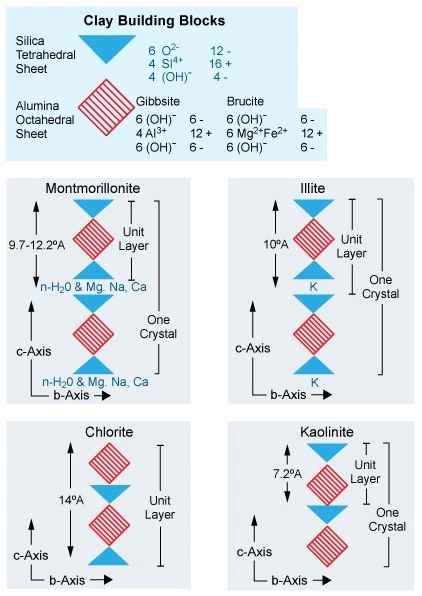

The Four Major Types of Clay Minerals
Montmorillonite (Smectite)
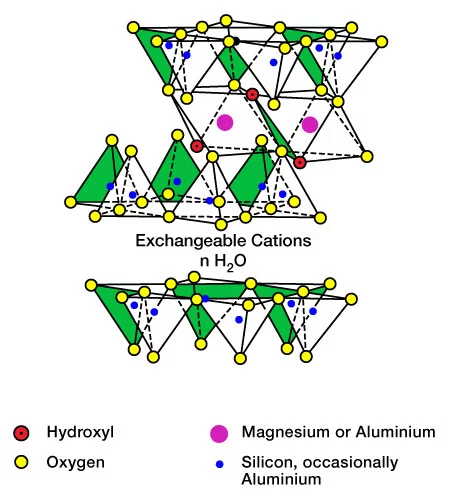
Montmorillonite (Figure 3) is a member of the smectite family of swelling clay minerals. Smectites have a large chemically active surface area, a high cation exchange capacity and inter-lamellar surfaces with extreme hydration characteristics. When this clay imbibes fresh water, it swells to several times its original volume and retains a significant amount of water between the layers in its mineral structure. This change in volume can cause montmorillonite clays to dislodge and migrate within the pore system, resulting in plugged pore throats, which usually cause a dramatic permeability reduction.
Illite
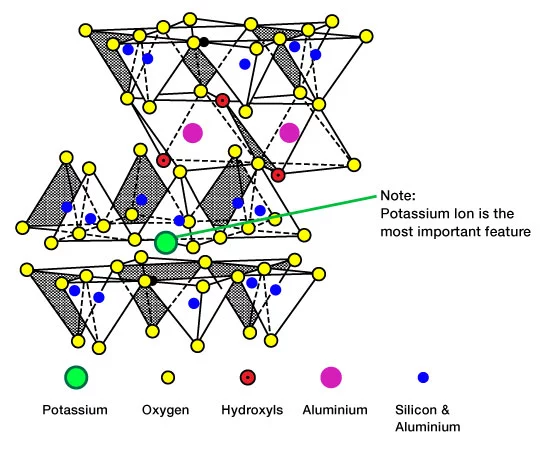
Illite clays (Figure 4) commonly appear as fibrous masses of fine crystals. Illite is often associated with the migration of fines, along with a reduction in permeability. High values of microporosity and immobile bound water saturation are often associated with illite clays.
Kaolinite
Kaolinite (Figure 5) commonly occurs in the pore system as discrete particles in the form of large flaky booklets, which do not attach securely to sand grain surfaces. When kaolinite booklets become dislodged, they are usually too large to fit through pore throat openings, and therefore, are often responsible for clogging pore throats.

Chlorite
Chlorite (Figure 6) commonly occurs as a pore lining around individual sand grains or in clusters. Chlorite often contains significant amounts of iron and magnesium within its structure.

When clays are found to contain a combination of clay minerals, they are termed mixed-layer clays.
Clay Classification According to Grain Size
Clay can also be defined as a sedimentary particle of any composition that is smaller than a very fine silt grain, having a diameter of less than 1256 mm (4 microns). The Wentworth Scale classifies particles by setting a standard definition of grain size, based on its diameter. Table 1 shows the relevant parts of the Wentworth Scale.
| Particle Type | Grade Limits (mm) | Grade Limits (microns) | Aggregate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Range: from 2 to 0.625 mm | Range: from 2000 to 50 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Very coarse sand | 2 to 1 mm | 2000 to 1000 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Coarse sand | 1 to 1/2 mm | 1000 to 500 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Medium sand | 1/2 to 1/4 to mm | 500 to 250 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Fine sand | 1/4 to 1/8 mm | 250 to 125 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Very fine sand | 1/8 to 1/16 mm | 125 to 63 microns | Sand / Sandstone |
| Silt | Range: from 0.05 to 0.004 mm | Range: from 50 to 4 microns | Silt / Siltstone |
| Coarse silt | 1/16 to 1/32 mm | 63 to 31 microns | Silt / Siltstone |
| Medium silt | 1/32 to 1/64 mm | 31 to 16 microns | Silt / Siltstone |
| Fine silt | 1/64 to 1/128 mm | 16 to 8 microns | Silt / Siltstone |
| Very fine silt | 1/128 to 1/256 mm | 8 to 4 microns | Silt / Siltstone |
| Clay | Range: less than 0.004 mm | Range: less than 4 microns | Clay / Shale |
| Coarse clay | 1/256 to 1/512 mm | 4 to 2 microns | Clay / Shale |
| Medium clay | 1/512 to 1/1024 mm | 2 to 1 microns | Clay / Shale |
| Fine clay | 1/1024 to 1/2048 mm | 1 to 0.5 micron | Clay / Shale |
This classification scheme does not distinguish between grains of clay minerals and other similarly sized grains that are not composed of clay minerals. Therefore, the Wentworth classification does not account for the unique petrophysical properties that set clay minerals apart from other particles of the same size.
Clay Classification According to Origin
Clays can be classified to reflect their mode of origin, either allogenic (detrital) or authigenic:
- Allogenic, or detrital, clays are deposited with the sandstone at the same time that the sediments are laid down. Examples of such clays are found in structural and laminated clays.
- Authigenic clays precipitate from solution at a later time, rather than being transported. Dispersed clays fit into this class of authigenic clays.
There is an important distinction between detrital and authigenic clays in sandstones. Detrital clays tend to be trapped between the grains and are not part of the effective pore network. Authigenic, dispersed clays are located within the pore system and, due to their very large surface area relative to the detrital framework grains (Table 2), have an impact on the chemical sensitivity and petrophysical properties of the sandstone, which is disproportionate to their volumetric contribution.
| Mineral | Surface Area |
|---|---|
| Quartz | 0.15 |
| Smectite | 752 |
| Illite | 113 |
| Chlorite | 42 |
| Kaolinite | 23 |
Table 2: Nitrogen Absorption Measurements Comparing
Specific Surface Areas of Quartz and Various Clay Minerals
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



