Assignment Cement Additives
What casing pressure at the point of injection is needed to open a gas lift valve with the following specifications, where the tubing pressure at the point of injection (Pprod) is 420 psi?
Part A:
- The casing will be cemented in a single stage.
- The density of “neat” Class H cement slurry (no additives) is 16.4 lb/gal.
- Formation pressure at the casing shoe is approximately 1,125 psi.
- Fracture pressure gradient is estimated at 0.795 psi/ft.
Note that at the conclusion of cement displacement, this formation must be able to support a column of cement that extends from 2500 feet back to the surface.
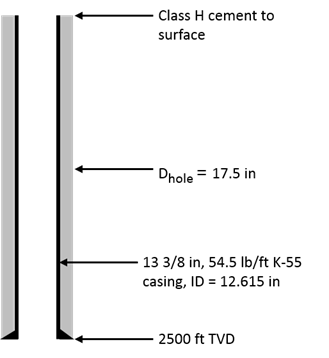
Perform the necessary calculations to answer the following question:
Based on the hydrostatic pressure of the Class H neat cement, do you need to add an extender to the Class H slurry? (Assume a safety margin of 0.5 lb/gal Equivalent Density.)
Part B:
Bentonite is a commonly used extender.
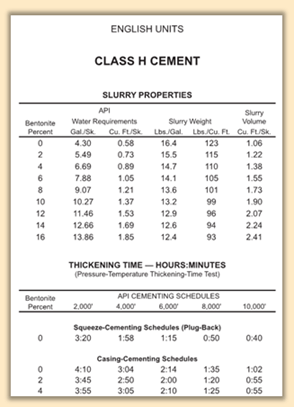
Referring to the Slurry Properties of Class H Cement table (Halliburton eRedbookTM), how many pounds of bentonite should be added to each sack of cement? (1 sack of dry Class H cement weighs 94lb.)
Solution
Part A Solution:
Fracture pressure at shoe: 0.795 psi/ft × 2500 ft=1988 psi
Hydrostatic pressure of fluid column: 0.052×TVD×Density
Safety margin: 0.052 × 2500 × 0.5= 65 psi
Fracture pressure including safety margin: 1988 − 65=1923 psi
Equivalent density of fracture pressure: 1923/(.052×2500)=14.8 lb/gal
Part B Solution:
As you solved in Part A, the slurry density for this job must be equal to or less than 14.8lbgal.
In the table, the bentonite concentration that will come closest to the required density is 4%.
Weight of bentonite per sack of cement: 0.04×94=3.76 lb/sack
Assessment
1. Which of the following materials can be used to prevent lost circulation?
A .Manganese tetraoxide
B .Ilmenite
C .Cellophane flakes ✔
D .Montmorillonite
2. A common antifoaming agent for cement is _________.
A .azodicarbonamide
B .ethylene glycol ✔
C .titanium hydride
3. The use of cement additives ensures that the cement operation meets critical criteria. Which of the following attributes are critical to a successful cement operation? (Select all that apply.)
A .Remains pumpable until properly placed in the well. ✔
B .Does not damage the formation. ✔
C .Sets uniformly, bonding securely to casing and formation. ✔
D .Sets within two hours.
E .Does not cool down.
4. The most commonly used cement accelerator is ____________ .
5. Identify some examples of strengthening agents. (Select all that apply.)
A .particulated rubber ✔
B .nylon fibers ✔
C .polyethylene glycol
D .metallic microribbons ✔
E .silicone emulsions
Recommended for You
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



