Assignment 1
Cement Slurry and Post-flush Fluid Volumes
Using the data provided, calculate the quantity of cement slurry and post-flush fluid required to cement the intermediate string of casing in the Assignment Well. Include a 25% cement contingency.
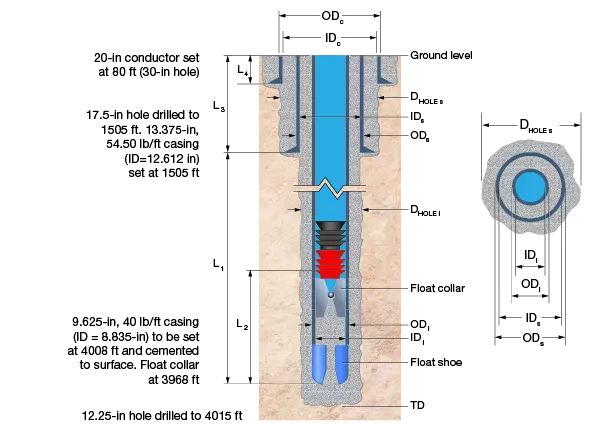
| Casing String | Hole Diameter Dhole (in) | Hole Depth* (feet) | Casing Shoe Depth* L (feet) | Depth to Float Collar* (feet) | Casing OD (in) | Casing ID (in) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductor [c] | 30 | 40 | L4 = 80 | N/A | 20 | 19 |
| Surface [s] | 17.5 | 1510 | L3 =1505 | 1465 | 13.375 | 12.615 |
| Intermediate [i] | 12.25 | 4015 | 4008 | 3968 | 9.625 | 8.835 |
Summary Table
Solution
Answers:
Volume of cement, ft3: 1546 cf
Post-flush fluid volume, ft3: 1689 cf
Solution:
1. Volume of casing/opening hole annulus (VAnnulus−1):
![]()
![]()
2. Volume of casing/opening hole annulus (VAnnulus−2):
![]()
![]()
3. Volume of cement left inside the casing (Vcsg):
![]()
![]()
4. Volume of cement in open hole below casing (VOH):
![]()
![]()
Total slurry volume: 1550 cf or 276 Bbl
Displacement volume:
![]()
![]()
Assignment 2
Fluid Density
Using the information in the table below and the relationships covered in the subject, calculate the missing values.
| Fluid | ppg | |
| Water | 62.4 | |
| Salt Water | 8.95 | |
| Cement | 15.6 |
Solution
Using this relationship: ![]()
| Fluid | ppg | |
| Water | 62.4 | 8.34 (62.4/7.48) |
| Salt Water | 66.95 (8.95 x 7.48) | 8.95 |
| Cement | 116.69 (15.6 x 7.48) | 15.6 |
Assignment 3
Fluid Density
Calculate the pressure gradient (![]() ) and bottomhole pressure (psi) in the intermediate string of casing of the Assignment Well when filled with the fluids shown in the table.
) and bottomhole pressure (psi) in the intermediate string of casing of the Assignment Well when filled with the fluids shown in the table.
Depth = 2015 ft
Calculate the missing values in the following table:
| Fluid | Pressure Gradient ( | Bottomhole Pressure (psi) |
| Water (62.4 | ||
| Salt Water (8.95 ppg) | ||
| Cement (15.6 ppg) |
Solution
Data:
Depth(h): 2015 ft
Patm: 14.7 psi
Density:
- Water: 62.4

- Salt water: 8.95 ppg
- Class A cement slurry: 15.6 ppg
Formula:
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Fluid | Pressure Gradient ( | Bottomhole Pressure (psi) |
| Water (62.4 | 0.433 = (62.4/144) | 887.2 = (14.7+0.433×2015) |
| Salt Water (8.95 ppg) | 0.465 = ((8.95/144)×7.48) | 951.7 = (14.7+0.465×2015) |
| Cement (15.6 ppg) | 0.810 = ((15.6/144)×7.48) | 1646.9 = (14.7+0.810×2015) |
Assignment 4
Use the data shown here to answer the questions.
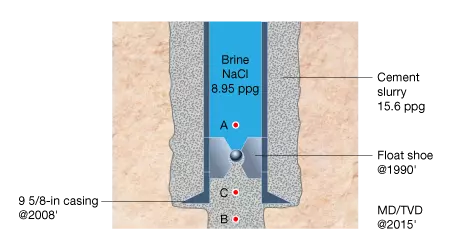
A. What is the absolute pressure in the brine column at point A just above the float shoe?
B. What is the absolute pressure at point B, the bottom of the hole, within the cement column?
C. What is the pressure at point C just below the shoe, at 1990 ft?
Solution
Solution to A:
Since the fluid down to point A is brine, the weight of the fluid above it is 8.95 ppg
![]()
![]()
Answer: ![]()
Solution to B:
Since the cement fills the annulus down to point B is cement, the weight of the fluid above it is 15.6 ppg
![]()
![]()
Answer: ![]()
Solution to C:
Since the fluid at point C is also in the cement column, the weight of the fluid above it is 15.6 ppg
![]()
![]()
Answer: ![]()
Assessment
1. Identify customary oilfeld units of volume that are used in cementing operations. (Select all that apply.)
A .Barrel ✔
B .Cubic foot ✔
C .Cubic inch
D .Cubic yard
E .Gallon
2. The most basic process for accomplishing a primary cementing job employs what method?
A .Two-wiper plug method ✔
B .Three-wiper plug method
C .One-wiper plug method
3. Which of these statements regarding cement volume calculations are TRUE? (Select all that apply.)
A .Displacement fluid volumes should be calculated to ensure that the cement slurry is displaced to the top of the float shoe.
B .It is uncommon to cement surface casing all the way to surface.
C .It is important to leave enough cement in and around the bottom of the casing to ensure the integrity of the cement bond. ✔
D .A contingency factor is often included in cement volume estimates to account for borehole diameters that are larger than the nominal bit diameter. ✔
4. As with most regulatory agencies, the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection requires that job logs be available for onsite inspection. What cementing-related items are typically required on a job log? (Select all that apply.)
A .Compressive strength of cement
B .Core analysis
C .Pumping rates, pressures, and duration ✔
D .Mix water pH and temperature ✔
E .Cement density ✔
5. What are the main reasons for primary cementing? (Select all that apply.)
A .To seal off lost circulation zones during drilling
B .To repair damaged casing
C .To abandon a depleted producing zone
D .To protect the casing connections
E .To restrict fluid movement between subsurface formations ✔
F .To anchor the casing to the formation ✔
6. In a typical primary cementing job, cement slurry is pumped into the ________ and displaced into the ___________, from the bottom to at least the top of the producing zones, and sometimes to the surface.
A .formation; annulus
B .casing; annulus ✔
C .annulus; casing
7. ____________ is the expected pressure in the wellbore formations created by the continuous presence of water in interconnected pores from the formation to the surface.
A .Overburden pressure
B .Wellbore pressure
C .Fracture pressure
D .Hydrostatic pressure ✔
8. The presence of salt in water __ its density.
A .has no effect on
B .increases
C .decreases
9. Because the density of sedimentary rock is about 2.5 x that of water, the pressure gradient imposed by the weight of the overburden is estimated to be about _ psi/ft of depth.
A .4
B .3
C .2
D .1 ✔
10. Pressure is the force exerted on a unit area. In what units can pressure be expressed? (Select all that apply.)
A .psf ✔
B .psi ✔
C .bar ✔
D .kPa ✔
E .ppg
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



