Underbalanced Well Classification System
A classification system developed by the International Association of Drilling Contractors’ Underbalanced Operations Committee was issued in Spring 2001. The main purpose of this classification system is to establish a reference database of wells drilled with different underbalance levels and techniques.
The classification system is presented in the form a matrix (Table 1).
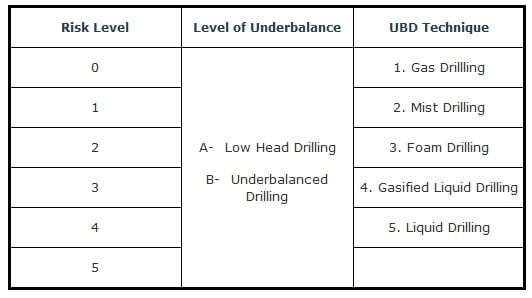
The first part of the system identifies the well in terms of associated risk levels, as defined in Table 2. Following the risk level identifier, a sub-classifier is used to define whether the well is drilled underbalanced or with a “low head”. The last component of the notation identifies the type of underbalanced drilling technique used (Table 3).
| Risk Level | Identification |
|---|---|
| 0 | Performance enhancement only; no hydrocarbon containing zones. |
| 1 | Well incapable of natural flow to surface. Well is “inherently stable” and is low level risk from a well control point of view. |
| 2 | Well is capable of natural flow to surface but enabling conventional well kill methods and limited consequences in case of catastrophic equipment failure. |
| 3 | Geothermal and non-hydrocarbon production. Maximum shut-in pressures less than UBD equipment operating pressure rating. Catastrophic failure has immediate serious consequences. |
| 4 | Hydrocarbon production. Maximum shut-in pressures less than UBD equipment pressure rating. Catastrophic failure has immediate serious consequences. |
| 5 | Maximum projected surface pressures exceed UBD operating pressure rating but are below BOP stack rating. Catastrophic failure has immediate serious consequences. |
| UBD Technique | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gas Drilling | The overall process of drilling using only gas as the drilling medium. No intentional fluid added. |
| Mist Drilling | Drilling with liquid entrained in a continuous gaseous phase. Typical mist systems have less than 2.5% liquid content. |
| Foam Drilling | Drilling with a two-phase fluid with a continuous liquid phase generated from the addition of liquid, surfactant, and gas. Typical foams range from 55% to 97.5% gas. |
| Gasified Liquid Drilling | Drilling with a gas entrained in a liquid phase. |
| Liquid Drilling | Drilling with a single-phase liquid. |
For example, a vertical section of a geothermal well drilled in a known formation with a low head nitrogen-lightened drilling fluid would be classified as: 3-A-4.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



