Drilling Mud Effects on the Fluid Saturation
Water Base Muds
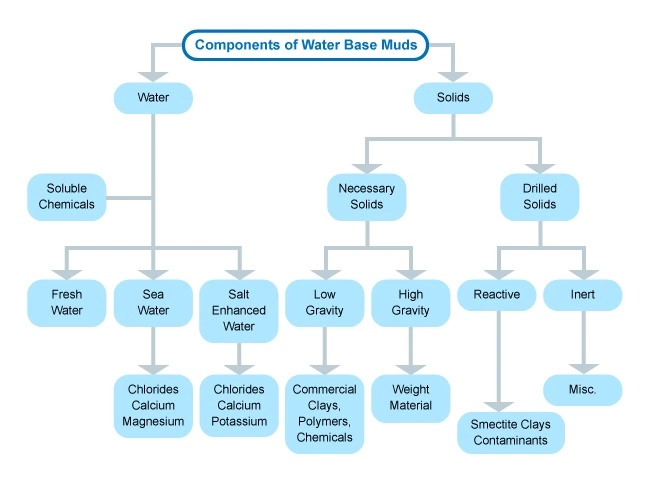
Water base drilling muds (Figure 1) have a range of additives, clays and chemicals incorporated into the water to create a homogeneous blend. The clay is usually a combination of native clays that are suspended in the fluid while drilling, or specific types of clay such as bentonite. Barite is commonly used to increase the mud weight (Figure 2). Many different chemicals can be added to a water base mud system to achieve drilling operational efficiencies (Figure 3). Water is the continuous phase.


In general, the use of water base drilling muds results in a moderate diameter of invasion, and thus a measurable invaded zone. In cases where the water loss is excessively high or the mud column highly overbalanced, invasion diameters can be quite large. In such instances, the measurement of Rxo is easy, but that of Rt is more difficult, and the corresponding value for Sw is less reliable.
Most importantly, the mud filtrate invasion is always water. This water will replace moveable hydrocarbons within the invaded zone, with a consequential increase in the water saturation of the invaded formation.
Oil Base Muds
Oil base drilling muds, in general, have oil as their continuous phase and water as the dispersed phase in conjunction with emulsifiers, wetting agents and gellants. The oil base can be diesel, kerosene, fuel oil, selected crude oil or mineral oil. The water phase of oil base mud can be fresh water, or a solution of sodium or calcium chloride. The external phase is oil and does not allow the water to contact the formation. Components of oil base drilling muds are shown in Figure 4.

Oil base drilling mud systems generally produce an oil filtrate. In water-bearing formations, the relative permeability to oil is often low, and invasion is slight. In oil-bearing formations, reservoir oil may be replaced by invading oil filtrate, and normally not any of the formation water is displaced. Consequently, Sxo is likely to be equal to Sw when oil base muds are used. Most importantly, oil is the mobile phase.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



