Learning Objectives
After completing this topic “Clays, Shales and Non-Clay Contributors to Low Resistivity“, you will be able to:
- Define clays and shales.
- Describe how clays are classified.
- Summarize the various ways that clays and shales can be distributed within reservoirs and the corresponding effects on well log interpretation.
- Discuss how non-clay materials contribute to low resistivity well log readings.
Overview of Clays and Shales
This discussion of clays and shales refers to their role in low resistivity well log interpretation in conventional resource reservoirs.
The various clay grains (Figure 1) within shale formations have been identified as a leading cause of low resistivity pays.

While it may be difficult to distinguish clay from shale with many logging while drilling (LWD) and wireline log tool measurements, it is clays that complicate the log analysis of low resistivity pay zones. In this course, clays and shales will be examined, together with the various chemical, mineralogical and structural factors which interact to lower the response of deep resistivity logging tools in pay zones.
Definitions of clays and shales
Shale Definition
Shale (Figure 2) is a fine grained, indurated, detrital sedimentary rock formed by the consolidation, through either compression or cementation, of clay, silt, and mud. It is characterized by a finely stratified structure of laminae, often ranging from 0.1 to 0.4 mm in thickness. Shale contains an appreciable content of clay minerals or derivatives from clay minerals, with some detrital quartz. Shale normally contains at least 50% silt, with 35% clay or mica fraction and 15% chemical or authigenic materials.
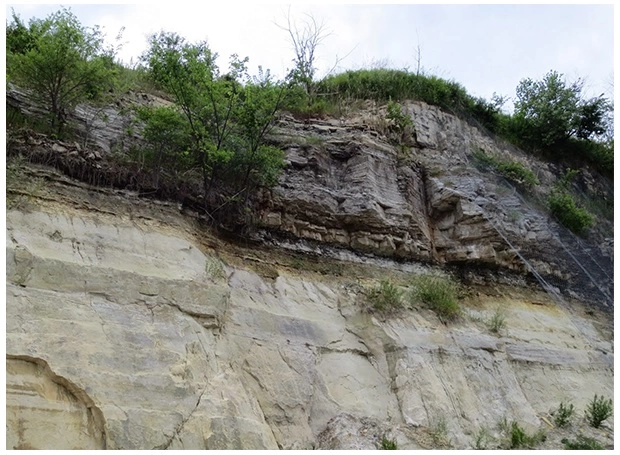

The term shale was originally applied only to laminated clayey rock, but now applies to thinly laminated or fissile claystone, siltstone, or mudstone (Figure 3). This term is sometimes used without any implication as to the shale’s composition, and has occasionally been somewhat loosely applied to massive or blocky indurated silts and clays that are not laminated, to laminated silts and clays that are not indurated, to fine-grained and thinly laminated sandstones, and to slates.

Clay Definition
Clay is a rock, mineral fragment, or a detrital particle of any composition that has a diameter of less than 1/256 mm (4 microns). This is approximately the upper size limit (Figure 4) at which a particle can show colloidal properties. It contains a considerable amount of clay minerals, (hydrous aluminum silicates) derived by weathering or by precipitation from feldspathic rocks. Clay also contains subordinate amounts of finely divided quartz, decomposed feldspar, carbonates, ferruginous matter, and other impurities. Furthermore, this composition should have more than 50% clay-sized particles, and clay minerals must form at least 25% of the total.

The term clay also applies to loose, earthy, extremely fine-grained natural sediment or soft rock composed primarily of clay-sized (Figure 5), or colloidal, particles that are characterized by their plasticity. It is commonly applied to any soft, adhesive, fine grained deposit and to earthy material.

It is easy to see why shale and clay are so often used interchangeably. Shale is related to clay through its composition, being a mixture of about half clay and half silt.
Effect of clays and shales on Well Logs
Shales
In shales, the silt component does not unduly affect the formation properties or the well log responses. The clay component does, however, significantly affect many of the well log responses. Any thorough log evaluation must account for the effects of shale and clay minerals. These effects reach well beyond a reduction in the resistivity response. Other petrophysical properties of shales and clays must be considered, such as their density, amount of hydrogen, radioactivity, permeability, and so forth.
The extent to which the log evaluation and the resulting estimation of the water saturation, Sw, is affected by clay or shale will depend on the type and volume, as well as the distribution, of shales and clays with respect to the pay sandstone.
Clays
Clays generally consist of hydrous alumino silicate minerals mixed with various other minerals and different proportions of silts. Any porosity found within clay will be affected by the particle arrangement and rock compaction. Its pore spaces most often contain water but may also contain hydrocarbons.
As with other lithologies, the log responses to clay will depend on its composition and porosity, as well as its water, or hydrocarbon, saturation. In a pore system, clay minerals are capable of exerting a disproportionate response compared to their volume, which is especially dramatic when applied to the resistivity log response.
Sandstones (Figure 6) with large amounts of clay, such as illite, can show very high values of well log calculated water saturations while still producing hydrocarbons free of water. This is due to the presence of bound water (Figure 7) within the micropores of clay minerals, as well as the surface conductivity of the clays and clay water system.

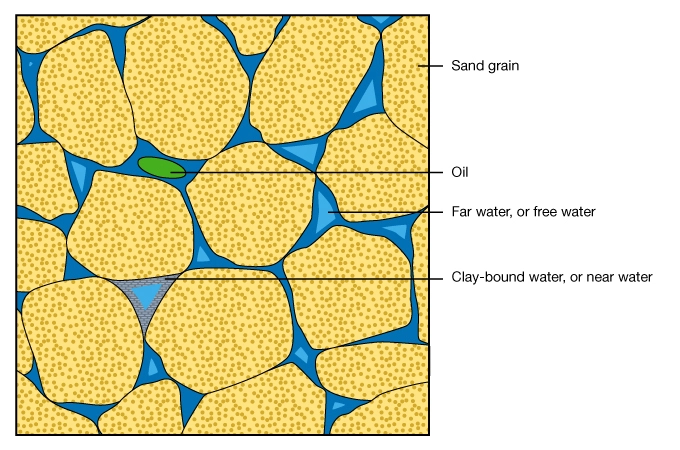
Many oilfield problems attributed to clays, such as borehole sloughing while drilling a well and reduced formation permeability, are caused by its interaction with water. Water in the molecular lattice of clay causes it to expand as water molecules squeeze between the lattice layers. This increases the volume of the clay particle, reduces its density, and often causes a reduction in the rock’s permeability. Clay expansion in water may also be responsible for shale sloughing in boreholes, and for the movement of fines.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.



