There are two general exploration situations that influence prospect generation. The first situation involves frontier, or less mature basins, where the presence of hydrocarbons ...
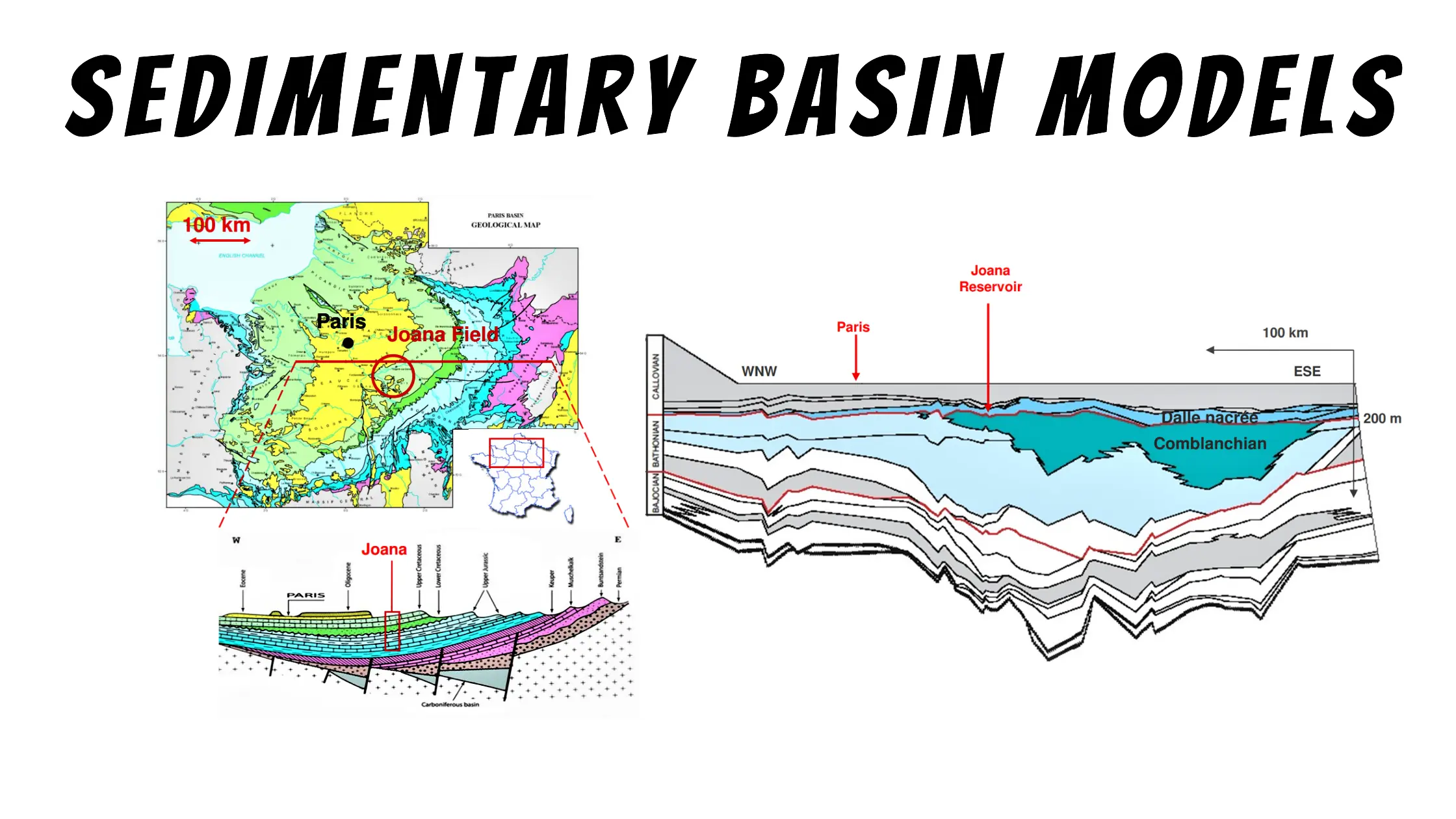
Read More »Sedimentary Basin Models
Stratigraphy now incorporates many topics normally assigned to other subdisciplines within the earth sciences, and we are in the midst of an evolution of stratigraphic analysis termed quantitative dynamic stratigraphy. In quantitative dynamic stratigraphy (QDS) ...
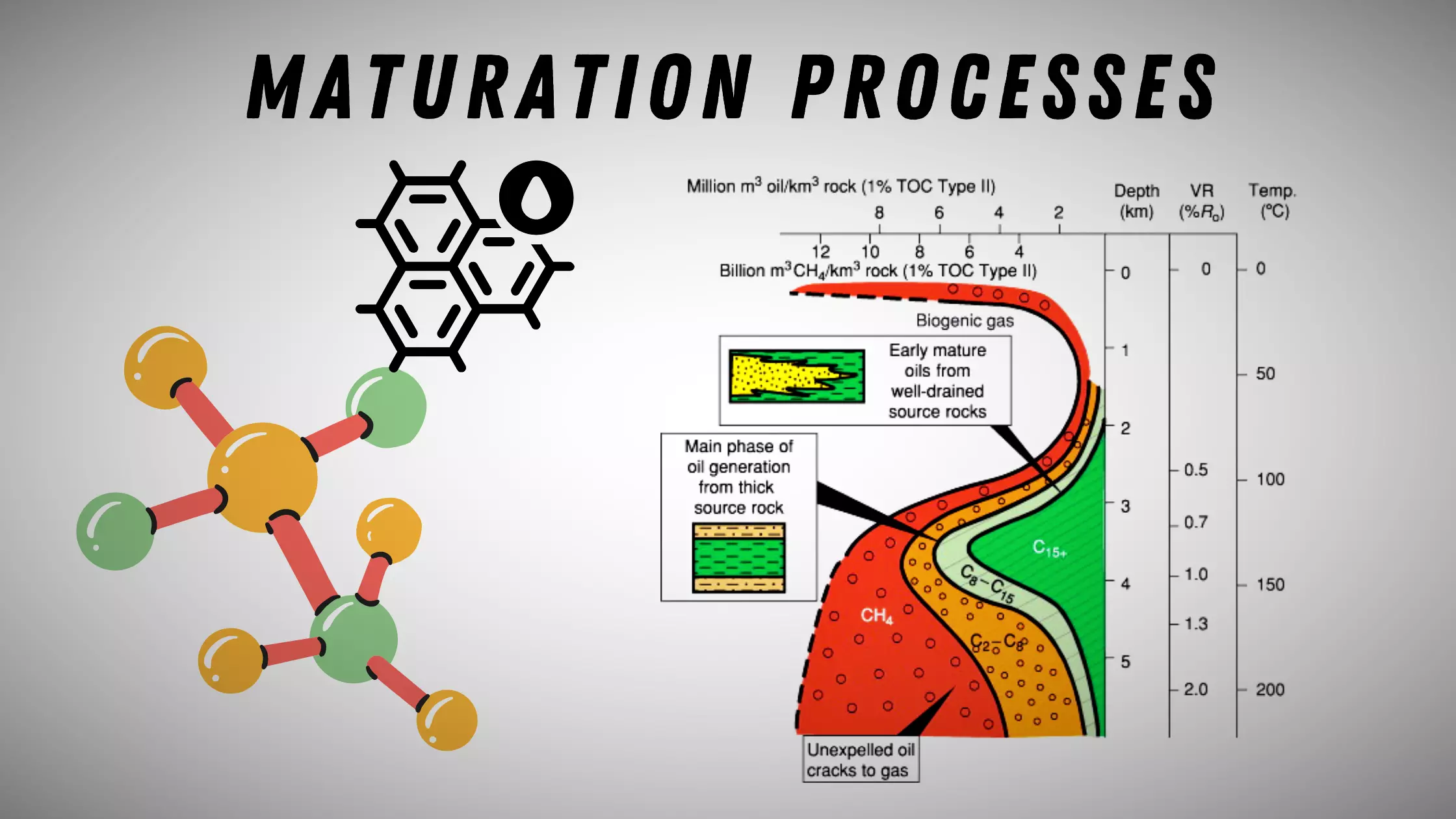
Read More »Maturation Processes
Maturation processes refer to the natural physical and chemical changes that occur in organic matter over time as it is buried deeper and subjected to higher temperatures and pressures. These processes are important in petroleum geology because they can lead to the formation of hydrocarbons (oil and gas) from organic-rich …
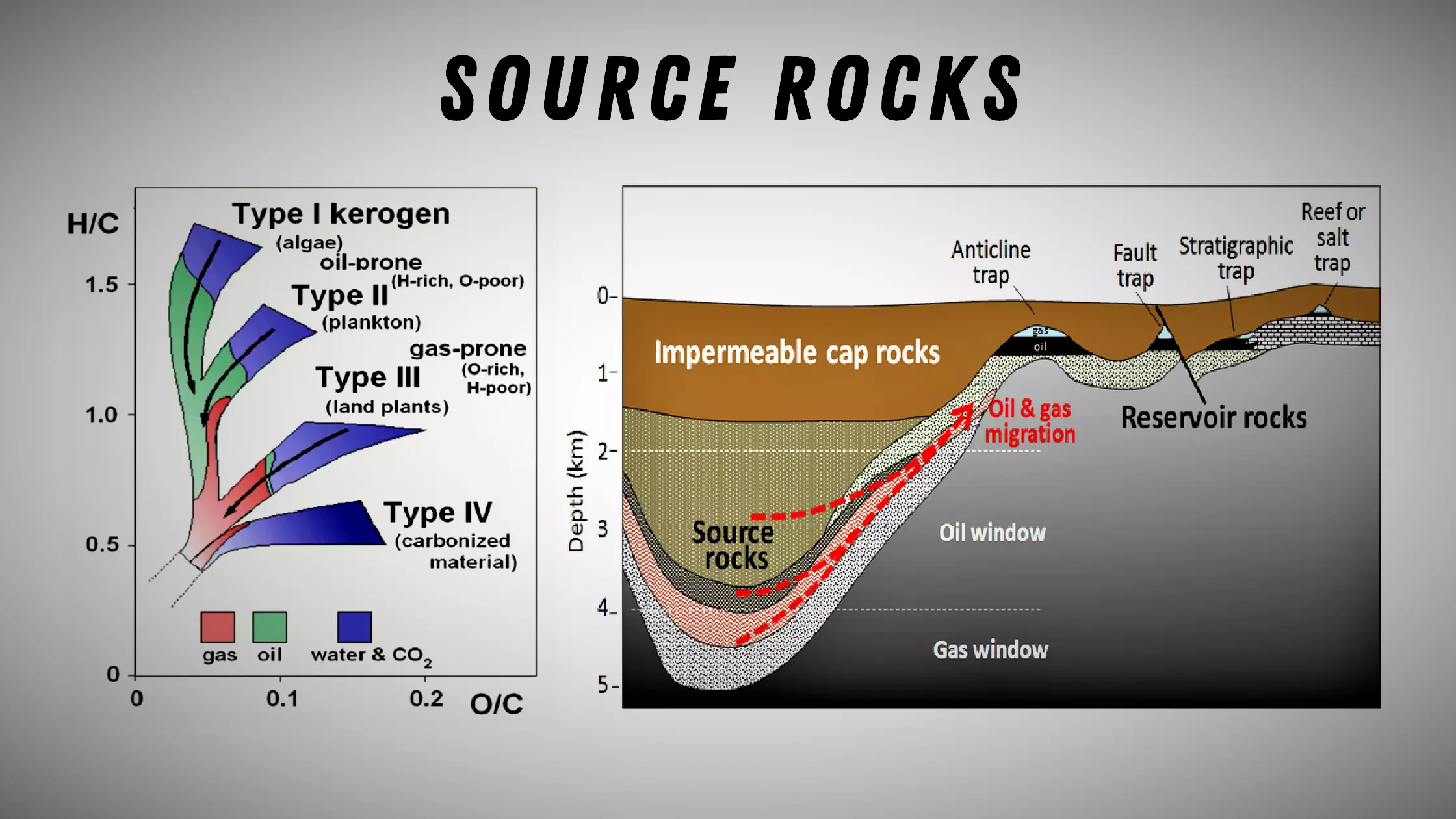
Read More »Source Rocks: The Origin of Petroleum
Source rocks are rocks that contain sufficient organic material to create hydrocarbons when subjected to heat and pressure over time. Source rocks ...
Read More »Geodynamic Models
Geodynamic models are process/response models that estimate subsidence and heat flow histories of basins. We use these models to estimate values, like maturation levels or ...
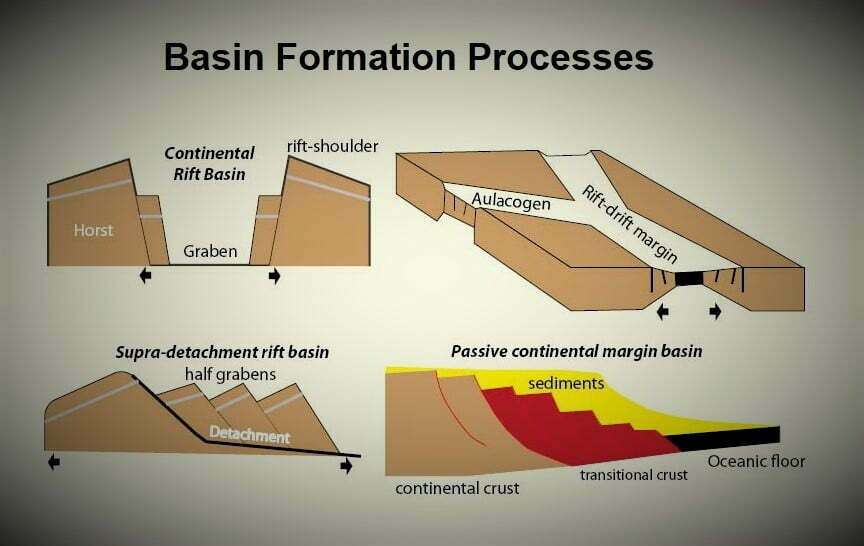
Read More »Basin Formation Processes
Sedimentary basins form in response to tectonic processes, such as heating events and tectonic loading. These processes control the temporal and spatial evolution of subsidence. Changes in the shape of the basin as ...
Read More »Basin Analysis and Petroleum Analysis
As we explore for hydrocarbons we must ask ourselves many questions: Are hydrocarbon source rocks present? When were hydrocarbons generated?
Read More » Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.