Carbonate Matrix Acidizing Treatments
In matrix acidizing, HCl is injected into the formation below fracturing pressure. The objective of such a treatment is to achieve radial acid penetration and increase permeability near the wellbore. The main application for this technique is to remove near wellbore damage and restore productivity in highly permeable zones.
A major problem in carbonate acidizing is that HCl usually reacts too fast. Generally, the main factors that affect HCl reaction rate on limestone and dolomite are area/volume ratio and diffusion.
Area/Volume Ratio: HCl reaction time is indirectly proportional to the carbonate surface area in contact with the acid. Extremely high area/volume ratios are the general rule in matrix acidizing. Therefore, obtaining significant acid penetration before spending during a matrix treatment is almost impossible. Figure 1 (effect of area-volume ratio on HCl-CaCO3 reactions) shows the comparative effect of area/volume ratio on HCl spending time in a 6-in.
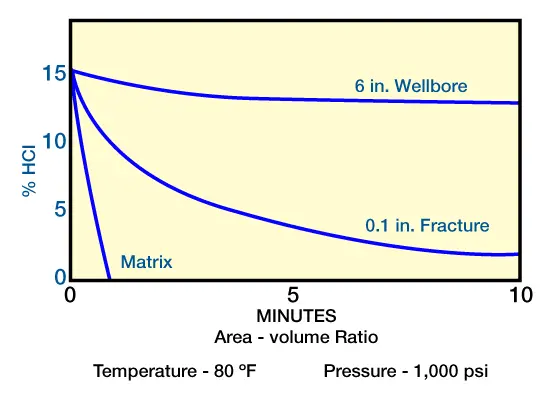
wellbore 0.1-in. fracture, and matrix of a limestone formation.
Diffusion: Diffusion is the time required for spent HCl on the formation surface to be replaced by live acid in solution.
Well Candidates
Carbonate formations damaged during drilling or completion are generally the best candidates for matrix acidizing treatments, because natural production can usually be restored. In some cases, however, other types of treatment may be equally effective.
If the formation is homogeneous, such that an induced fracture will heal, hydraulic fracturing with proppant may be a better stimulation choice. Nearby water zones would definitely be a factor in considering a matrix treatment, but, again, a low-injection fracture acidizing treatment may yield better results.
For example, consider a fracture acidizing treatment designed for significantly increasing production and minimizing bottom water production. This design involved a well with a 60-ft perforated interval in a carbonate formation 200 ft above an oil-water contact. There were two choices in attempting to stay away from the water: (1) a true matrix acidizing treatment and (2) a controlled height fracture acidizing treatment designed at a low injection rate. Matrix acidizing provides the best chance that only the perforated interval is treated, but would require a whopping 180,000 gal of HCl to dissolve a 5-ft wellbore radius. In contrast, fracture acidizing at 12 BPM with a viscous preflush and 30,000 gal of HCl would create an etched fracture length of approximately 200 ft. The created flow capacity is more or less equivalent to a 100-ft effective wellbore radius.
Acidizing Considerations
Only a few special considerations need discussion in most cases of carbonate formation acidizing. To maximize production, acid types and additives need to be carefully selected. From the standpoint of reaction with formation minerals, however, there is little chance of doing more harm than good to production. Table 1 provides some useful guidelines for acid selection.
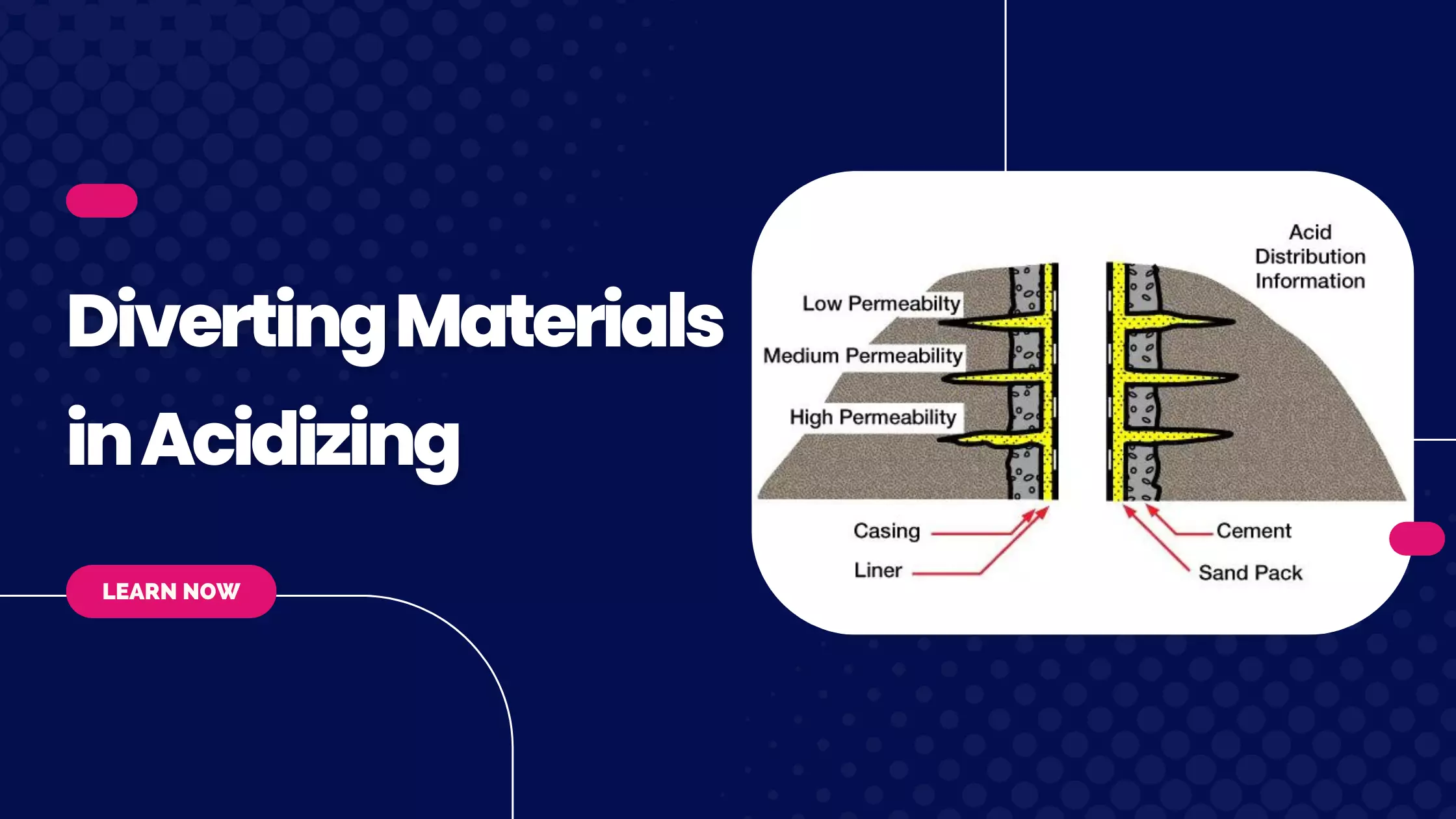
When HCl is injected into a carbonate reservoir under matrix conditions, acid preferentially flows into the areas of highest permeability. Acid reaction in the high-permeability regions causes the development of large, highly conductive flow channels called wormholes (Figure 2 , carbonate core with large wormholes). High reaction rates, as observed between all concentrations of HCl and carbonates, tend to favor wormhole creation.
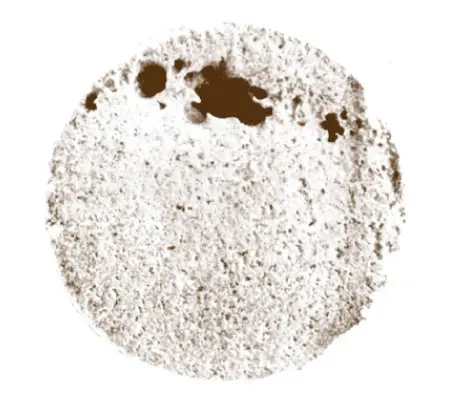

Wormhole length normally is controlled by the fluid-loss rate from the wormhole to the formation matrix. It can be substantially increased by reducing the fluid loss rate from the worm-hole to the formation with fluid-loss additives. The careful selection of type and concentration of additive is essential. For example, too high a concentration of fluid-loss additive can plug the formation, and too little is not effective.
The most effective fluid-loss additives are solids or acidswellable polymers used in fracture acidizing. Emulsified acids, because of their high viscosity, often give better results than plain HCl. On the other hand, retarded acids usually work no better than HCl in a matrix treatment because they do not control the rate of fluid loss from a wormhole.
Treatment Design
The design of a matrix acidizing treatment for a carbonate formation consists of specifying acid type and volume, a maximum injection rate, and fluid pressure that will not fracture the formation. The same calculation method used to determine maximum injection rate and pressure in matrix acidizing of sandstone applies here. Selection of acid type and volume, however, are more arbitrary.
| Situation | Acid Type |
|---|---|
| Perforating Fluid | 5% Acetic |
| Damaged Perforations | 10% Formic |
| 10% Acetic | |
| 15% HCl | |
| Deep Wellbore Damage | 15% HCl |
| 28% HCl | |
| Emulsified HCl |
A good general recommendation is to inject 50 to 200 gal/ft of 15% or 28% HCl. Exact acid volume and strength cannot be predicted without knowing specific near-wellbore conditions. A good general rule would be to use larger acid volume in high-temperature wells (or where deep damage is suspected), and high-strength HCl with an effective fluid-loss additive in zones where acid can be injected at practical rates of 0.25 to 0.5 BPM.
 Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.
Petro Shine The Place for Oil and Gas Professionals.